Definition, Origin, History, Philosophy, Logic, Usage, and Benefits
Introduction
The word taxonomy is widely used in science, education, information systems, and digital platforms. At its core, taxonomy refers to the practice of classification—organizing things into structured groups to make them easier to understand, manage, and use. From biology to websites and databases, taxonomy plays a crucial role in how humans organize knowledge.
Definition of Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science or system of classifying and organizing concepts, objects, or living organisms into categories based on shared characteristics.
In simple terms:
Taxonomy is a structured way to name, group, and organize things.
Etymology of the Word “Taxonomy”
The word taxonomy comes from Greek roots:
- Taxis (τάξις) – meaning arrangement or order
- Nomos (νόμος) – meaning law or rule
Combined, taxonomy literally means:
“The law of arrangement”
This reflects its purpose: creating rules for how things should be classified.
Origin of Taxonomy
The concept of taxonomy originated from the human need to organize knowledge. Early civilizations categorized plants, animals, and objects for survival, medicine, and trade.
However, taxonomy as a formal discipline began in the 18th century, primarily in the field of biology.
History of Taxonomy
Early History
- Ancient Greek philosophers like Aristotle classified animals based on physical traits.
- Early systems were simple and often based on appearance or function.
Modern Taxonomy
- The modern foundation of taxonomy was laid by Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778).
- He introduced a systematic method of classification and naming known as binomial nomenclature.
- Linnaeus’s work made taxonomy standardized, scientific, and globally accepted.
Since then, taxonomy has expanded beyond biology into fields like:
- Library science
- Linguistics
- Computer science
- Information architecture
- Digital content management
Philosophy of Taxonomy
Philosophically, taxonomy is about how humans understand reality. It reflects how we:
- Identify similarities and differences
- Define relationships between concepts
- Create meaning through structure
Taxonomy assumes that order improves understanding and that knowledge becomes more useful when it is well organized.
Logic Behind Taxonomy
The logic of taxonomy is based on:
- Hierarchy (parent → child relationships)
- Similarity and difference
- Consistency
- Clarity
A good taxonomy follows logical rules so that users can:
- Predict where information belongs
- Navigate systems intuitively
- Avoid confusion or duplication
Usage of Taxonomy
Today, taxonomy is used across many domains:
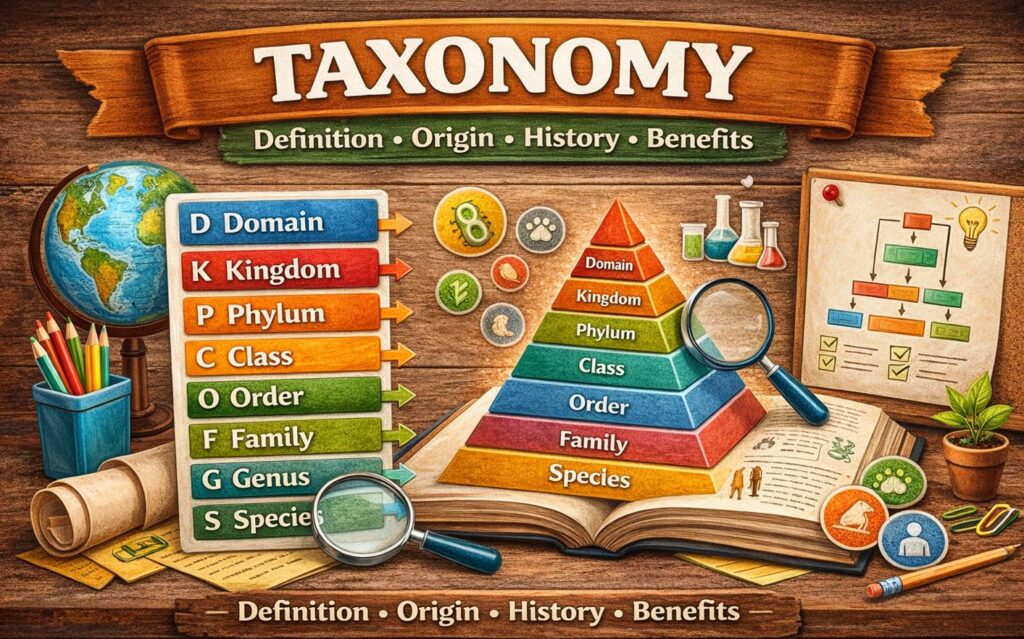
1. Biology
- Classifying living organisms (kingdom, phylum, class, etc.)
2. Education & Research
- Organizing academic subjects and knowledge areas
3. Websites & Digital Platforms
- Categories, tags, menus, and content structures
- Examples: blog categories, product categories, directories
4. Libraries & Archives
- Cataloging books, documents, and media
5. Business & Marketing
- Segmenting products, customers, and services
Benefits of Taxonomy
Using taxonomy offers many advantages:
✅ Improved Organization
- Information becomes structured and easy to manage
✅ Better Navigation
- Users can quickly find what they are looking for
✅ Enhanced Understanding
- Complex information becomes simpler and clearer
✅ Scalability
- Systems can grow without becoming chaotic
✅ SEO & Discoverability
- Well-defined categories improve search engine visibility
✅ Decision Making
- Clear classification supports better analysis and planning
Taxonomy in the Digital Age
In modern digital platforms, taxonomy is essential for:
- Content management systems (like WordPress)
- E-commerce websites
- Search engines
- Data classification and AI systems
Without taxonomy, digital information becomes disorganized and difficult to use.
Conclusion
Taxonomy is more than just a technical term—it is a fundamental way humans organize knowledge and make sense of the world. From its Greek origins to its modern digital applications, taxonomy continues to shape how information is structured, accessed, and understood.
Whether in science, business, or web design, a strong taxonomy creates clarity, efficiency, and value.
I
Leave a Reply